Imagine a world where you can feel the texture of a virtual object or sense the impact of a virtual punch. Welcome to the realm of tactile feedback and haptic technology, where touch becomes an essential part of the digital experience. The article “Beyond The Screen: The Rise Of Tactile Feedback And Haptic Technology” explores the growing prominence of these technologies and their potential to revolutionize how we interact with virtual environments. Get ready to discover a new dimension of immersion as you dive into the realm of touch.
The History of Haptic Technology
Early Beginnings
Haptic technology, often referred to as the science of touch, has a fascinating history that stretches back thousands of years. The earliest evidence of haptic technology can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where tactile feedback was used in various ways. For example, the Egyptians used hieroglyphics that depicted the sensation of touch, demonstrating an early recognition of the importance of tactile communication.
Advancements in Vibrating Technology
One significant advancement in haptic technology came with the invention of vibrating devices in the late 19th century. The first practical implementation of haptic feedback was seen in the telegraph industry, where vibrating devices were used to provide tactile feedback to telegraph operators. The vibrating devices were designed to alert operators to incoming messages, improving their efficiency and reducing errors.
The Emergence of Tactile Feedback
The concept of tactile feedback, where users receive physical sensations in response to their interactions with devices, gained popularity in the 20th century. In the 1960s, researchers began exploring the use of tactile feedback in human-computer interaction. This led to the development of the first haptic devices, such as joysticks and force feedback controllers, which allowed users to feel the virtual environments they were interacting with.
The Integration of Haptic Technology into Devices
As technology progressed, so did haptic technology. Today, haptic feedback is seamlessly integrated into various devices and applications. From smartphones and gaming consoles to virtual reality headsets and medical simulators, haptic technology has become an integral part of the user experience. With advancements in haptic actuators, sensors, and algorithms, developers now have more control over the precision and complexity of haptic feedback, further enhancing the user’s sense of touch.
Understanding Haptic Technology
What is Haptic Technology?
Haptic technology, often referred to as haptics, is a branch of technology that focuses on the sense of touch. It aims to recreate the sensation of touch and provide users with a tactile experience when interacting with devices. Haptic technology utilizes various types of actuators, sensors, and software to deliver physical sensations, enabling users to feel textures, vibrations, forces, and even temperature changes.
How Haptic Feedback Works
Haptic feedback works by using actuators to generate mechanical vibrations or forces that can be sensed by the user. These actuators can be electromechanical devices, such as vibration motors, or electrostatic systems that create frictional forces. Sensors, such as accelerometers and force sensors, capture the user’s interactions, providing input for the haptic system to generate appropriate feedback. The integration of software algorithms allows for the precise control and synchronization of haptic effects, enhancing the realism of the tactile experience.
Types of Haptic Feedback
There are various types of haptic feedback that can be experienced. The most common ones include vibrations, which simulate the sensation of objects shaking or pulsing, and force feedback, which provides resistance or pressure in response to user interactions. Other types include texture feedback, which recreates the feeling of different surfaces, and temperature feedback, which can simulate hot or cold sensations. The combination of these different types of feedback allows for a more immersive and realistic user experience.
Benefits of Haptic Technology
Haptic technology offers several benefits that enhance the user experience. Firstly, it provides a new dimension of interaction by adding physical sensations to visual and auditory cues. This can greatly enhance immersion and realism in gaming, virtual reality, and other digital experiences. Haptic feedback also improves communication and interactivity, as users can receive feedback or notifications without having to rely solely on visual or auditory cues. Additionally, haptic technology has proven to increase engagement and emotional connection, making the user experience more memorable and impactful.
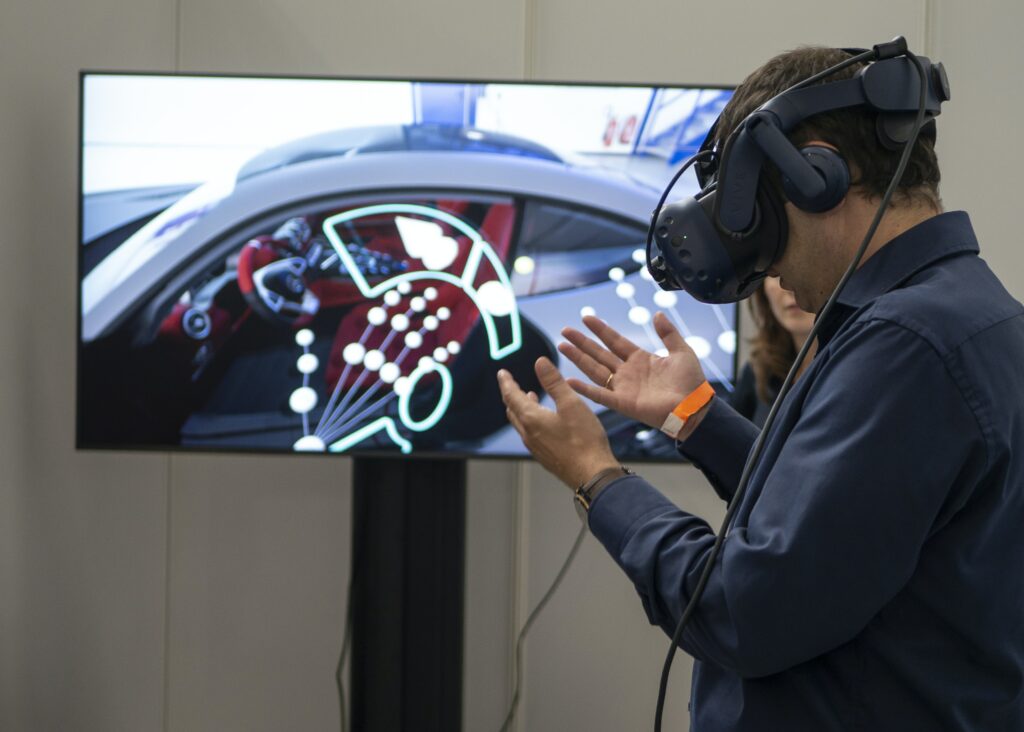

Applications of Haptic Technology
Haptic Feedback in Gaming
One of the most popular and widespread applications of haptic technology is in gaming. Haptic feedback in gaming controllers, such as rumble motors, provides users with tactile sensations that enhance gameplay. For example, when a player’s character is hit or encounters an obstacle, the controller can vibrate, providing a more immersive and dynamic gaming experience. This type of feedback not only adds realism but also improves gameplay by allowing players to feel the environment and their actions within the game.
Haptic Technology in Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) has revolutionized the way we experience digital content, and haptic technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the realism of VR experiences. VR haptic gloves or controllers can provide users with tactile feedback, allowing them to feel the virtual objects they interact with. Whether it’s feeling the texture of a virtual surface or sensing the impact of virtual objects, haptic feedback in VR adds a whole new level of immersion and presence to the virtual world.
Haptic Feedback in Medical Training
Haptic technology has found valuable applications in the field of medical training. Medical simulators equipped with haptic feedback enable trainees to practice surgical procedures and other medical interventions in a realistic and safe environment. By providing the tactile and force feedback associated with real-life procedures, haptic simulators enhance the learning experience and improve trainee performance. With haptic technology, medical professionals can hone their skills and improve patient outcomes without the need for patient involvement during the training process.
Haptic Interfaces in Automotive Industry
Haptic interfaces have made their way into the automotive industry, transforming the driving experience. Features such as haptic feedback in touchscreens and steering wheel vibrations enhance driver safety and improve interaction with in-vehicle systems. For example, haptic feedback can help drivers keep their eyes on the road by providing tactile confirmation when buttons or controls are activated, reducing distractions. Additionally, haptic feedback can simulate the feel of different surfaces on touchscreen interfaces, making them easier to navigate without visual attention.
Haptic Technology in Mobile Devices
Haptic feedback has become a standard feature in modern mobile devices. Smartphones and tablets utilize haptic actuators to provide tactile feedback for interactions such as typing on virtual keyboards or pressing virtual buttons. Haptic feedback in mobile devices offers users a more engaging and precise typing experience, mimicking the sensation of physical buttons. It also allows for the creation of distinct feedback patterns, such as different vibrations for notifications or alerts, further enhancing the user’s ability to differentiate between different events.
The Science behind Tactile Feedback
Sensory Perception and Haptic Sensation
Sensory perception plays a crucial role in the way we interact with the world, and haptic sensation is an essential component of our sensory experience. The skin, our largest organ, is rich in receptors that detect different tactile stimuli such as pressure, vibration, temperature, and texture. The brain processes these signals and assigns meaning to them, allowing us to perceive the physical properties of objects and environments. Haptic technology seeks to replicate and manipulate these sensations to create realistic and compelling experiences.
Psychophysics of Haptic Perception
Psychophysics is the branch of psychology that studies the relationship between physical stimuli and the psychological responses they elicit. In the context of haptic technology, psychophysics explores how humans perceive and interpret different haptic feedback. Researchers examine factors such as the intensity, duration, and frequency of vibrations or forces to determine their perceptual effects on the user. By understanding the psychophysics of haptic perception, developers can optimize the design and implementation of haptic feedback systems to create more accurate and enjoyable experiences.
Neuroscience and Tactile Feedback
The field of neuroscience has contributed valuable insights into our understanding of tactile perception and the neural mechanisms involved in haptic sensation. Neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), enable researchers to map brain activity while participants engage with haptic stimuli. These studies have revealed specific brain regions and neural circuits involved in processing haptic feedback, helping researchers refine their understanding of tactile perception and develop more precise haptic feedback algorithms.
Advancements in Tactile Material Science
Tactile material science is an area of research focused on developing innovative materials and surfaces that can simulate different haptic sensations. Scientists and engineers are continuously exploring new materials and fabrication techniques that can reproduce realistic textures and feedback. For example, researchers have developed flexible displays that can change their shape to create tactile feedback or surfaces with embedded microtextures that can simulate the feeling of different materials. The advancements in tactile material science have a direct impact on the development of haptic technologies and enable more immersive and realistic user experiences.

The Future of Haptic Technology
Enhanced Haptic Feedback Systems
The future of haptic technology holds the promise of even more advanced and realistic haptic feedback systems. Ongoing research aims to improve the precision, responsiveness, and complexity of haptic actuators and sensors. By incorporating more degrees of freedom and finer control over vibrations, forces, and textures, haptic feedback systems will be able to provide users with an even more immersive and realistic tactile experience.
Innovations in Wearable Haptic Devices
Wearable haptic devices, such as haptic gloves and suits, offer exciting possibilities for the future of haptics. These devices can provide users with full-body haptic feedback, allowing for more comprehensive and engaging experiences. For example, haptic gloves can simulate the feeling of holding and manipulating objects in virtual reality, while haptic suits can create the sensation of being touched or impacted by virtual entities. As technology continues to evolve, wearable haptic devices will become more lightweight, affordable, and widespread.
Augmented Reality and Haptic Technology
As augmented reality (AR) gains traction, the integration of haptic technology will become crucial in creating truly immersive AR experiences. Haptic feedback can complement the visual and auditory cues of AR by providing users with tactile sensations associated with virtual objects and environments. Imagine being able to feel the texture of an augmented object or receiving tactile guidance in a virtual navigation system. The combination of AR and haptic technology has the potential to revolutionize industries such as education, design, and entertainment.
Haptic Technology in Robotics and Prosthetics
Haptic technology has already made significant advancements in the field of robotics and prosthetics. Robots equipped with haptic sensors and actuators can interact with their environment more effectively, enabling tasks that require a delicate touch, such as surgical procedures or industrial assembly. Similarly, prosthetic limbs enhanced with haptic feedback systems can provide users with a natural sense of touch, allowing for more intuitive and precise control. As haptic capabilities continue to evolve, the field of robotics and prosthetics will witness groundbreaking advancements.
Challenges and Potential Solutions
While the future of haptic technology is undoubtedly exciting, it also comes with its share of challenges. Technical limitations, such as power consumption, size constraints, and response time, need to be overcome to achieve more advanced and efficient haptic systems. Standardization and compatibility across different devices and platforms are also vital to ensure widespread adoption and seamless integration of haptic technology. Cost and affordability remain a concern, particularly in consumer applications where high-quality haptics can be expensive. Lastly, user adaptation and the learning curve associated with haptic technology need to be addressed to maximize user acceptance and satisfaction.
Haptic Technology in Accessibility
Assistive Technology for the Visually Impaired
Haptic technology has the potential to greatly enhance accessibility for individuals with visual impairments. Devices such as haptic braille displays allow blind individuals to read digital content through tactile sensations. By providing tactile feedback corresponding to each braille character, these devices enable blind individuals to access written information more independently and efficiently. Additionally, haptic navigation systems can provide tactile guidance, allowing visually impaired individuals to navigate unfamiliar environments safely.
Haptic Feedback for Individuals with Motor Impairments
Haptic feedback can also play a crucial role in assisting individuals with motor impairments in their daily lives. Haptic interfaces can provide tactile cues to aid in activities such as typing on a keyboard or using an assistive device. By incorporating haptic feedback, these interfaces enable users with limited motor control to interact with devices more effectively, improving their access to digital content and enhancing their overall independence.
Improving User Experience for the Elderly
As the population ages, ensuring a positive user experience for older adults becomes increasingly important. Haptic technology can contribute to creating inclusive and user-friendly interfaces for older individuals. Tactile feedback can assist in reducing errors by providing physical confirmation of actions, enhancing the usability of digital devices. Additionally, haptic feedback can be used to simplify complex user interfaces by providing meaningful and intuitive tactile cues, making technology more accessible to older adults.
The Impact of Haptic Technology on User Experience
Enhancing Immersion and Realism
Perhaps one of the most significant impacts of haptic technology is its ability to enhance immersion and realism in various digital experiences. Whether it’s through gaming, virtual reality, or simulations, haptic feedback provides users with a more complete and engaging sensory experience. Feeling the impact of an explosion in a video game or the texture of a virtual object in a simulation adds depth and realism to the user’s interaction, making the experience more visceral and memorable.
Improving Communication and Interactivity
Haptic feedback also improves communication and interactivity in digital environments. By providing users with tactile feedback, haptic technology enables more intuitive and efficient interactions with devices and systems. For example, haptic cues can convey information about direction, urgency, or importance without the need for visual or auditory cues. This not only enhances the user experience but also allows for more effective and inclusive communication, benefiting individuals with sensory impairments or language barriers.
Increasing Engagement and Emotional Connection
Haptic technology has the power to increase engagement and emotional connection between users and digital content. By adding tactile feedback, haptic technology can evoke emotional responses and create a stronger connection to the experience. For example, haptic feedback in storytelling can enhance the emotional impact of a narrative by providing users with physical sensations that elicit empathy and understanding. This heightened emotional connection not only makes the experience more enjoyable but also enhances the overall impact and memorability.
Usability and User Satisfaction
Haptic feedback significantly improves usability and user satisfaction in digital interactions. By providing tactile cues and physical confirmation, haptic technology helps users navigate interfaces more easily and reduces the likelihood of errors. This enhances the overall usability of devices and applications, leading to increased user satisfaction. Moreover, the tactile dimension of haptic feedback creates a more tangible and intuitive user experience, making technology more approachable and enjoyable for users of all levels of expertise.
Ethical Considerations in Haptic Technology
Privacy and Data Collection
As haptic technology becomes more integrated into our daily lives, the collection and use of haptic data raise concerns about privacy and security. Haptic sensors and feedback systems can record and transmit data about users’ tactile interactions, potentially revealing sensitive information. Safeguarding this data and ensuring users’ privacy should be a top priority for developers and manufacturers. Strict data protection measures, informed consent, and transparent data policies are essential to maintaining user trust in haptic technology.
Potential for Addiction and Dependence
Like any technology, haptic technology comes with the potential for addiction and dependence. The immersive and engaging nature of haptic experiences can lead to excessive use and disconnection from reality. Developers and users alike need to be mindful of the potential negative consequences of haptic technology and promote responsible and balanced usage. Education and awareness about healthy technology habits are crucial to prevent addiction and maintain a healthy relationship with haptic devices.
Ethical Use of Haptic Feedback in Simulations
Haptic technology is widely used in simulations for various purposes, including medical training, military training, and entertainment. However, ethical considerations need to be taken into account when incorporating haptic feedback in simulations. Simulations that involve potentially harmful or distressing experiences should prioritize the well-being and safety of users. Proper guidance, informed consent, and debriefing procedures are important to ensure users’ emotional and psychological well-being when engaging with haptic simulations.
Challenges and Limitations of Haptic Technology
Technical Limitations and Constraints
Haptic technology faces various technical limitations that need to be addressed for further advancements. Power consumption and energy efficiency are critical considerations, especially in battery-powered devices. Size constraints and form factors can limit the implementation of haptic actuators and sensors in smaller devices. Moreover, response time and latency play a crucial role in user satisfaction, requiring continuous improvements in haptic technology to achieve real-time and seamless feedback.
Standardization and Compatibility
Standardization and compatibility are important challenges in haptic technology, particularly when it comes to cross-platform integration. Ensuring consistent experiences across different devices and platforms is crucial for widespread adoption. Establishing industry standards for haptic technology will facilitate interoperability and enable developers to create haptic experiences that can be enjoyed seamlessly on multiple devices.
Cost and Affordability
The cost of haptic technology remains a barrier to its widespread adoption. High-quality haptic actuators and sensors can be expensive, limiting their availability in consumer products. Cost reduction efforts, enhanced manufacturing processes, and economies of scale will be key to making haptic technology more affordable and accessible to a broader range of users.
User Adaptation and Learning Curve
Integrating haptic technology into devices and applications requires users to adapt to a new mode of interaction. The learning curve associated with haptic feedback may present challenges for some users, particularly those unfamiliar with the technology. Proper user education, intuitive interfaces, and clear instructions are essential to minimize user frustration and maximize the adoption and acceptance of haptic technology.
Conclusion
Haptic technology represents a significant advancement in human-computer interaction, adding a new dimension to our digital experiences. From its early beginnings in vibrating devices to the integration of haptic feedback into gaming, virtual reality, medical training, and various other applications, haptic technology has come a long way. With ongoing advancements in sensory perception, neuroscience, and tactile material science, the future of haptic technology holds immense potential for enhancing user experiences across industries. As we explore the possibilities and tackle the challenges, we can look forward to a world where our digital interactions are not only visual and auditory but also delightfully tactile.